Notes on the consolidated financial statements
V. Depreciation and amortization:
Tangible Assets
Depreciation on tangible fixed assets is provided to the extent of depreciable amount on the straight line (SLM) Method. Depreciation
is provided at the rates and in the manner prescribed in Schedule II to the Companies Act, 2013 except on some assets, where useful
life has been taken based on external / internal technical evaluation as given below:
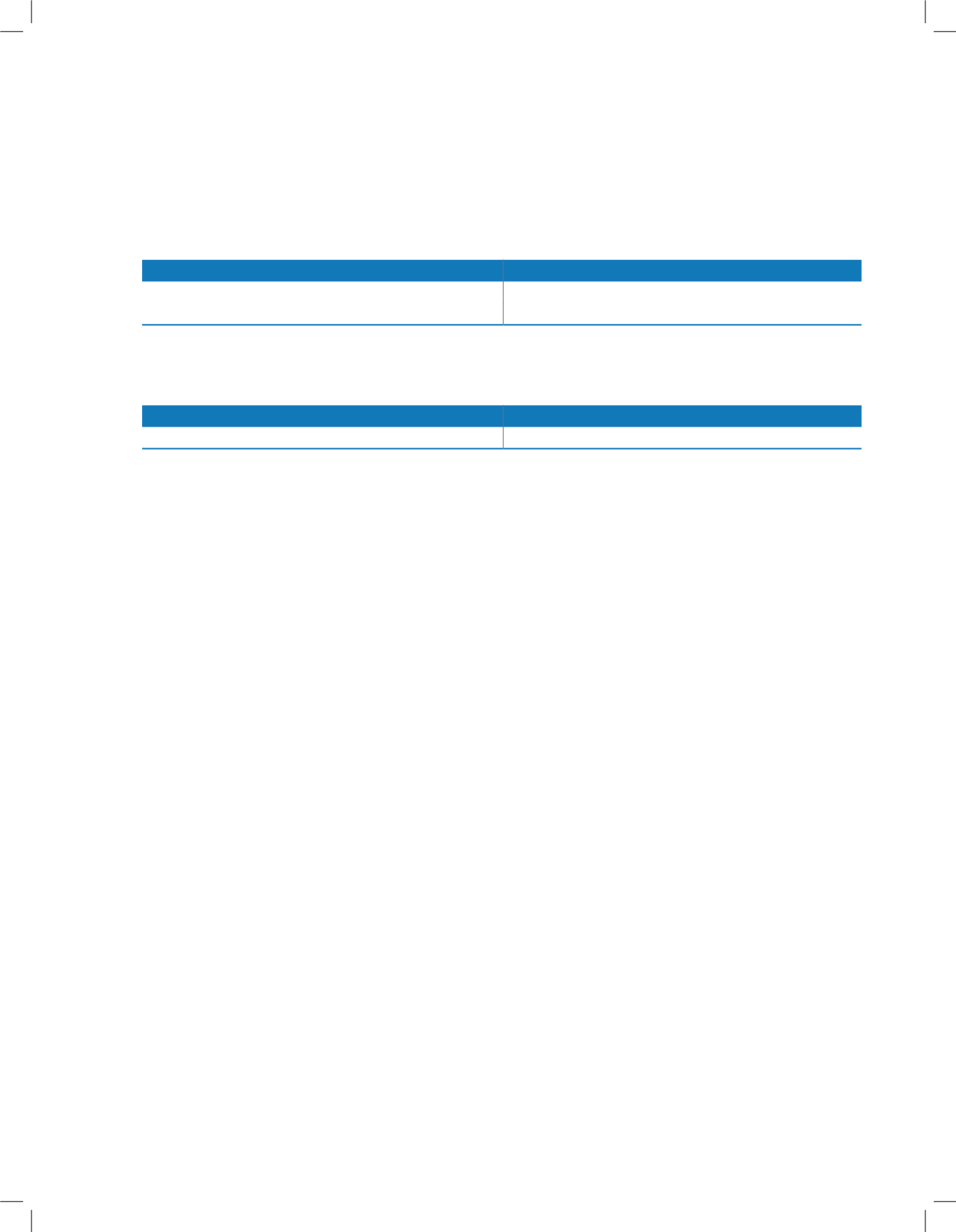
Particulars
Useful Life
Plant & machinery
7, 10 & 18 years
Fit-out and other assets at sales outlets
5 years
Leasehold land is amortized over the period of the lease.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are amortised over their estimated useful lives on straight line method as follows:
Particulars
Useful Life
Computer software
6 years
The estimated useful life of the intangible assets and the amortisation period are reviewed at the end of each financial year and the
amortisation period is revised to reflect the changed pattern, if any.
VI. Impairment:
The carrying values of assets /cash generating units at each balance sheet date are reviewed for impairment if any indication of
impairment exists. An asset is treated as impaired when the carrying cost of asset exceeds its recoverable value. An impairment loss is
charged to the Statement of Profit and Loss in the year in which an asset is identified as impaired. The impairment loss recognised in
prior accounting period is reversed if is a change in the estimate of recoverable amount.
VII. Investments:
Non-current investments are stated at cost. Provision for diminution in the value of long-term investments is made only if such a
decline is other than temporary.
VIII. Inventories:
Items of inventories are measured at lower of cost and net realizable value after providing for obsolescence, wherever considered
necessary. Cost of inventories comprises of cost of purchase, cost of conversion and other costs including manufacturing overheads
incurred in bringing them to their respective present location and condition.
Cost of raw materials, stores and spares, packing materials, trading and other products are determined on weighted average basis.
IX. Revenue Recognition:
Revenue is recognized only when risks and rewards incidental to ownership are transferred to the customer, it can be reliably measured
and it is reasonable to expect ultimate collection. Revenue from operations includes sale of goods, services and excise duty, adjusted
for discounts (net).
Dividend income is recognized when the right to receive payment is established.
Interest income is recognized on a time proportion basis taking into account the amount outstanding and the interest rate applicable.
X. Employee Stock Options:
Accounting value of stock options is determined on the basis of ‘Intrinsic Value’ representing the excess of the fair market value
of Company’s equity share on the date of grant over the exercise price of the options granted under the “Employees Stock Option
Scheme” of the Company, and is being amortised as “Employee Stock Compensation Cost” on a straight-line basis over the vesting
period in accordance with the Guidance Note on “Share Based Payments” issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
XI. Foreign Currency Transactions:
a) Foreign currency transactions are recorded at the exchange rates prevailing on the date of the transaction.
b) Monetary items denominated in foreign currencies at the year end are restated at year end exchange rates, except in cases covered
by forward contracts.
139
Annual Report 2015-16


